What is DeepFRI?¶
To get all the details please refer to original paper by Gligorijevic et. al. Structure-based protein function prediction using graph convolutional networks
Model overview¶
DeepFRI is a deep learning model for prediction of protein function from sequenece and structure. It consists of 2 parts:
Pretrained LSTM - a reccurent neural network pretrained on a large set of protein sequences.
Graph convolutional network - a neural network that allows for a representation of the protein structure as a graph.
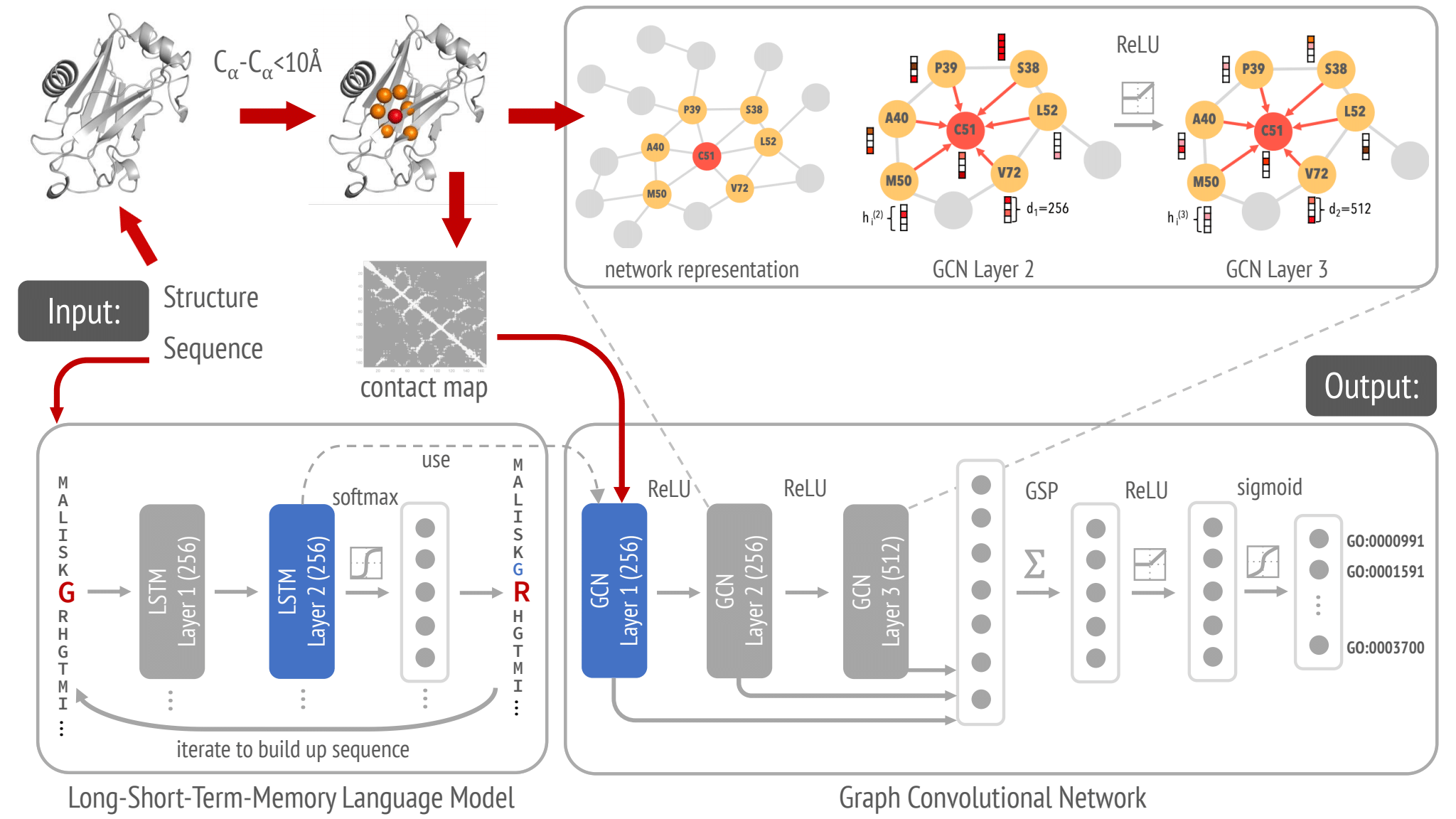
Pretrained LSTM¶
LSTM are a type of recurrent neural networks that is effective in sequence problems due to its ability to infer the relationship between elements of the sequence. This property explains their effectivity in many Natural Language Processing tasks.
LSTM was trained on a corpus of around 10 million protein domain sequences from Pfam. The pretraining task was to predict an amino acid residue in the context of its position in a protein sequence. In the final model, the parameters of the LSTM are frozen - it serves for to encode protein sequence embeddings.
Graph neural network¶
GCNs have proven to be powerful for extracting features from data that are naturally represented as one or more graphs. It was show to be a suitable method for extracting features from proteins by taking into account their graph-based structure of inter-connected residues, represented by contact maps.
Performance¶
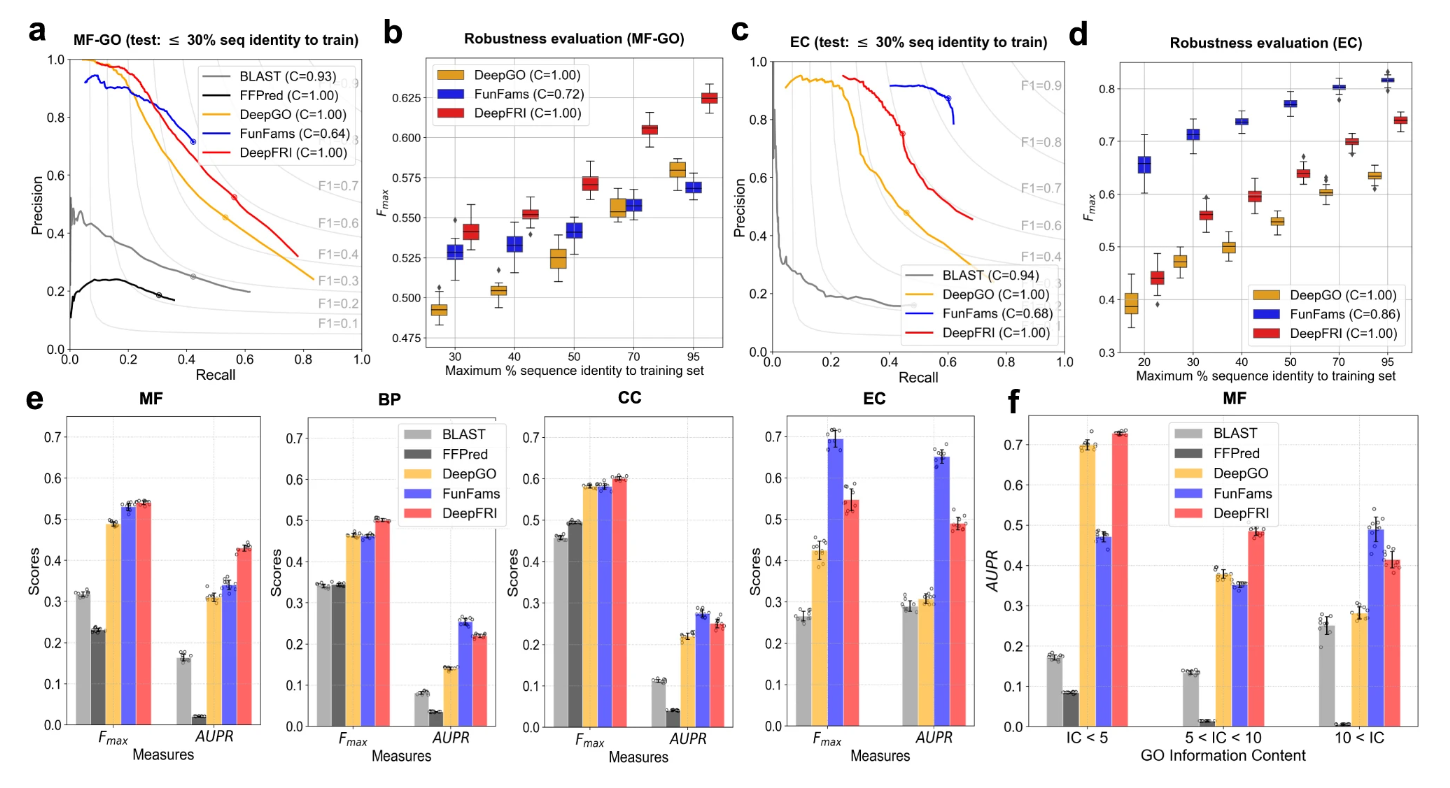
Every figure illustrates the performance of DeepFRI (red) in comparison to sequence-based annotation transfer from protein families, FunFams (blue), the CNN-based method DeepGO (orange), SVM-based method, FFPred (black), and BLAST baseline (gray). Precision-recall curves showing the performance of different methods on (a) MF-GO terms and (c) EC numbers on the test set comprised of PDB chains chosen to have ≤30% sequence identity to the chains in the training set. Distribution of the Fmax score under 100 bootstrap iterations for the top three best-performing methods applied on (b) MF-GO terms and (c) EC numbers computed on the test PDB chains and grouped by maximum % sequence identity to the training set. (e) Distribution of protein-centric Fmax score and function-centric AUPR score under 10 bootstrap iterations summarized over all test proteins and GO terms/EC numbers, respectively. (f) Distribution of AUPR score on MF-GO terms of different levels of specificities under 10 bootstrap iterations.